In ctype.h header file, there are many built in functions which are used to validate the data type of given variable and to convert to upper to lower case and lower to upper case.
Those functions are listed below
| Function | Description | Characters |
|---|---|---|
isalpha() |
check whether character is alphabetic | A; B; C; D; E; F; G; H; I; J; K; L; M; N; O; P; Q; R; S; T; U; V; W; X; Y; Z; a; b; c; d; e; f; g; h; i; j; k; l; m; n; o; p; q; r; s; t; u; v; w; x; y; z; |
isdigit() |
check whether character is digit | 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 0; |
isalnum() |
check whether character is alphanumeric | A; B; C; D; E; F; G; H; I; J; K; L; M; N; O; P; Q; R; S; T; U; V; W; X; Y; Z; a; b; c; d; e; f; g; h; i; j; k; l; m; n; o; p; q; r; s; t; u; v; w; x; y; z; 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 0; |
isspace() |
check whether character is space | tab; newline; vertical-tab; form-feed; carriage-return; space; |
islower() |
check whether character is lower case | a; b; c; d; e; f; g; h; i; j; k; l; m; n; o; p; q; r; s; t; u; v; w; x; y; z; |
isupper() |
check whether character is upper case | A; B; C; D; E; F; G; H; I; J; K; L; M; N; O; P; Q; R; S; T; U; V; W; X; Y; Z; |
isxdigit() |
check whether character is hexadecimal | 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 0; a; b; c; d; e; f; A; B; C; D; E; F; |
iscntrl() |
check whether character is control character | alert; backspace; tab; newline; vertical-tab; form-feed; carriage-return; NUL; SOH; STX; ETX; EOT; ENQ; ACK; SO; SI; DLE; DC1; DC2; DC3; DC4; NAK; SYN; ETB; CAN; EM; SUB; ESC; IS4; IS3; IS2; IS1; DEL; |
isprint() |
check whether character is printable character | A; B; C; D; E; F; G; H; I; J; K; L; M; N; O; P; Q; R; S; T; U; V; W; X; Y; Z; a; b; c; d; e; f; g; h; i; j; k; l; m; n; o; p; q; r; s; t; u; v; w; x; y; z; 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 0; tab; newline; vertical-tab; form-feed; carriage-return; space; exclamation-mark; quotation-mark; number-sign; dollar-sign; percent-sign; ampersand; asterisk; apostrophe; left-parenthesis;right-parenthesis; plus-sign; comma; hyphen; period; slash; colon; semicolon; less-than-sign; equals-sign; greater-than-sign; question-mark; commercial-at; left-square-bracket; backslash; circumflex; right-square-bracket; underline; grave-accent; left-curly-bracket; vertical-line; tilde; right-curly-bracket; |
ispunct() |
check whether character is punctuation | exclamation-mark; quotation-mark; number-sign; dollar-sign; percent-sign; ampersand; asterisk; apostrophe; left-parenthesis;right-parenthesis; plus-sign; comma; hyphen; period; slash; colon; semicolon; less-than-sign; equals-sign; greater-than-sign; question-mark; commercial-at; left-square-bracket; backslash; circumflex; right-square-bracket; underline; grave-accent; left-curly-bracket; vertical-line; tilde; right-curly-bracket; |
isgraph() |
check whether character is graphical character | A; B; C; D; E; F; G; H; I; J; K; L; M; N; O; P; Q; R; S; T; U; V; W; X; Y; Z; a; b; c; d; e; f; g; h; i; j; k; l; m; n; o; p; q; r; s; t; u; v; w; x; y; z; 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; 7; 8; 9; 0; exclamation-mark; quotation-mark; number-sign; dollar-sign; percent-sign; ampersand; asterisk; apostrophe; left-parenthesis;right-parenthesis; plus-sign; comma; hyphen; period; slash; colon; semicolon; less-than-sign; equals-sign; greater-than-sign; question-mark; commercial-at; left-square-bracket; backslash; circumflex; right-square-bracket; underline; grave-accent; left-curly-bracket; vertical-line; tilde; right-curly-bracket; |
tolower() |
convert alphabetic characters to lower case | A; B; C; D; E; F; G; H; I; J; K; L; M; N; O; P; Q; R; S; T; U; V; W; X; Y; Z; |
toupper() |
convert alphabetic characters to upper case | a; b; c; d; e; f; g; h; i; j; k; l; m; n; o; p; q; r; s; t; u; v; w; x; y; z; |
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
int main()
{
char c;
printf("Enter a character: ");
scanf("%c", &c);
if (isalnum(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not an alphanumeric character.", c);
else
printf("%c is an alphanumeric character.", c);
if (isalpha(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not an alphabetic character.", c);
else
printf("%c is an alphabetic character.", c);
if (isdigit(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a numeric character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a numeric character.", c);
if (isspace(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a space character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a space character.", c);
if (islower(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a lower case character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a lower case character.", c);
if (isupper(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a upper case character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a upper case character.", c);
if (isxdigit(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a hexadecimal character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a hexadecimal character.", c);
if (iscntrl(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a control character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a control character.", c);
if (isprint(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a printable character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a printable character.", c);
if (ispunct(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a punctuation character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a punctuation character.", c);
if (isgraph(c) == 0)
printf("%c is not a graphical character.", c);
else
printf("%c is a graphical character.", c);
return 0;
}
By default, the function isalpha, isdigit, isalnum, isspace,
islower, isupper, isxdigit, iscntrl, isprint,
ispunct, isgraph are defined as macros when ctype.h is included. For better performance, the
macro forms are recommended over the functional forms.
However, to get the functional forms, you can do one of these
- do not include ctype.h header file
- specify
#undef, for example,#undef islower - surround the call statement by parentheses, for example,
(islower)('a')
If you want to look at the source code of those functions, you can download glibc software on its official web glibc. The glibc version that I downloaded is glibc-2.27.
The macro forms of function isalpha, isdigit, isalnum, isspace, islower, isupper, isxdigit, iscntrl, isprint, ispunct, isgraph defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h look as follows
# define isalnum(c) __isctype((c), _ISalnum)
# define isalpha(c) __isctype((c), _ISalpha)
# define iscntrl(c) __isctype((c), _IScntrl)
# define isdigit(c) __isctype((c), _ISdigit)
# define islower(c) __isctype((c), _ISlower)
# define isgraph(c) __isctype((c), _ISgraph)
# define isprint(c) __isctype((c), _ISprint)
# define ispunct(c) __isctype((c), _ISpunct)
# define isspace(c) __isctype((c), _ISspace)
# define isupper(c) __isctype((c), _ISupper)
# define isxdigit(c) __isctype((c), _ISxdigit)
# define isblank(c) __isctype((c), _ISblank)
And the functional forms of function isalpha, isdigit, isalnum,
isspace, islower, isupper, isxdigit, iscntrl, isprint, ispunct, isgraph defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h declared in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h look as follows
__exctype (isalnum);
__exctype (isalpha);
__exctype (iscntrl);
__exctype (isdigit);
__exctype (islower);
__exctype (isgraph);
__exctype (isprint);
__exctype (ispunct);
__exctype (isspace);
__exctype (isupper);
__exctype (isxdigit);
__exctype (isblank);
__exctype is a macro function which is defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h as follows
#define __exctype(name) extern int name (int) __THROW
If we expand the macro, the declarations of function isalpha, isdigit, isalnum, isspace, islower, isupper, isxdigit, iscntrl, isprint, ispunct, isgraph will look as follows
extern int isalnum (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int isalpha (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int iscntrl (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int isdigit (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int islower (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int isgraph (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int isprint (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int ispunct (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int isspace (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int isupper (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int isxdigit (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
extern int isblank (int) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ ));
The function tolower and toupper are declared in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h as
follows
extern int tolower (int __c) __THROW;
extern int toupper (int __c) __THROW;
You can find the definitions of function isalpha, isdigit, isalnum, isspace, islower, isupper, isxdigit, iscntrl, isprint, ispunct, isgraph in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.c
#define func(name, type) \
int name (int c) { return __isctype (c, type); }
func (isalnum, _ISalnum)
func (isalpha, _ISalpha)
func (iscntrl, _IScntrl)
func (isdigit, _ISdigit)
func (islower, _ISlower)
func (isgraph, _ISgraph)
func (isprint, _ISprint)
func (ispunct, _ISpunct)
func (isspace, _ISspace)
func (isupper, _ISupper)
func (isxdigit, _ISxdigit)
If we expand the macro func, it will look as follows
int isalnum (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISalnum); }
int isalpha (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISalpha); }
int iscntrl (int c) { return __isctype (c, _IScntrl); }
int isdigit (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISdigit); }
int islower (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISlower); }
int isgraph (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISgraph); }
int isprint (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISprint); }
int ispunct (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISpunct); }
int isspace (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISspace); }
int isupper (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISupper); }
int isxdigit (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISxdigit); }
The definition of function isblank is defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype-c99.c
int
isblank (int c)
{
return __isctype (c, _ISblank);
}
__isctype is a macro which is defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h as follows
# define __isctype(c, type) \
((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) type)
If we expand the macro __isctype, it will look as follows
int isalnum (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISalnum); }
int isalpha (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISalpha); }
int iscntrl (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _IScntrl); }
int isdigit (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISdigit); }
int islower (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISlower); }
int isgraph (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISgraph); }
int isprint (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISprint); }
int ispunct (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISpunct); }
int isspace (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISspace); }
int isupper (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISupper); }
int isxdigit (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISxdigit); }
int isblank (int c) { return ((*__ctype_b_loc ())[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISblank); }
_ISalpha, _IScntrl, _ISdigit, _ISlower, _ISgraph,
_ISprint, _ISpunct, _ISspace, _ISupper, _ISxdigit and
_ISblank are the values of an enum without identifier defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h.
enum
{
_ISupper = _ISbit (0), /* UPPERCASE. */
_ISlower = _ISbit (1), /* lowercase. */
_ISalpha = _ISbit (2), /* Alphabetic. */
_ISdigit = _ISbit (3), /* Numeric. */
_ISxdigit = _ISbit (4), /* Hexadecimal numeric. */
_ISspace = _ISbit (5), /* Whitespace. */
_ISprint = _ISbit (6), /* Printing. */
_ISgraph = _ISbit (7), /* Graphical. */
_ISblank = _ISbit (8), /* Blank (usually SPC and TAB). */
_IScntrl = _ISbit (9), /* Control character. */
_ISpunct = _ISbit (10), /* Punctuation. */
_ISalnum = _ISbit (11) /* Alphanumeric. */
};
_ISbit is a macro function which is also defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h.
#define _ISbit(bit) ((bit) < 8 ? ((1 << (bit)) << 8) : ((1 << (bit)) >> 8))
Expanding the macro _ISbit, it becomes as follows
enum
{
_ISupper = ((0) < 8 ? ((1 << (0)) << 8) : ((1 << (0)) >> 8)), /* UPPERCASE. */
_ISlower = ((1) < 8 ? ((1 << (1)) << 8) : ((1 << (1)) >> 8)), /* lowercase. */
_ISalpha = ((2) < 8 ? ((1 << (2)) << 8) : ((1 << (2)) >> 8)), /* Alphabetic. */
_ISdigit = ((3) < 8 ? ((1 << (3)) << 8) : ((1 << (3)) >> 8)), /* Numeric. */
_ISxdigit = ((4) < 8 ? ((1 << (4)) << 8) : ((1 << (4)) >> 8)), /* Hexadecimal numeric. */
_ISspace = ((5) < 8 ? ((1 << (5)) << 8) : ((1 << (5)) >> 8)), /* Whitespace. */
_ISprint = ((6) < 8 ? ((1 << (6)) << 8) : ((1 << (6)) >> 8)), /* Printing. */
_ISgraph = ((7) < 8 ? ((1 << (7)) << 8) : ((1 << (7)) >> 8)), /* Graphical. */
_ISblank = ((8) < 8 ? ((1 << (8)) << 8) : ((1 << (8)) >> 8)), /* Blank (usually SPC and TAB). */
_IScntrl = ((9) < 8 ? ((1 << (9)) << 8) : ((1 << (9)) >> 8)), /* Control character. */
_ISpunct = ((10) < 8 ? ((1 << (10)) << 8) : ((1 << (10)) >> 8)), /* Punctuation. */
_ISalnum = ((11) < 8 ? ((1 << (11)) << 8) : ((1 << (11)) >> 8)) /* Alphanumeric. */
};
So the value of each of enum values is as follows
enum
{
_ISupper = 256, /* UPPERCASE. */
_ISlower = 512, /* lowercase. */
_ISalpha = 1024, /* Alphabetic. */
_ISdigit = 2048, /* Numeric. */
_ISxdigit = 4096, /* Hexadecimal numeric. */
_ISspace = 8192, /* Whitespace. */
_ISprint = 16384, /* Printing. */
_ISgraph = 32768, /* Graphical. */
_ISblank = 1, /* Blank (usually SPC and TAB). */
_IScntrl = 2, /* Control character. */
_ISpunct = 4, /* Punctuation. */
_ISalnum = 8 /* Alphanumeric. */
};
__ctype_b_loc is a function returning to pointer to pointer to const unsigned short int which
is declared in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.h.
extern const unsigned short int **__ctype_b_loc (void)
__THROW __attribute__ ((__const__));
and defined in glibc-2.27/include/ctype.h
CTYPE_EXTERN_INLINE const uint16_t ** __attribute__ ((const))
__ctype_b_loc (void)
{
return __libc_tsd_address (const uint16_t *, CTYPE_B);
}
Macro CTYPE_EXTERN_INLINE is expanded as extern inline defined in glibc-2.27/include/ctype.h.
Macro __libc_tsd_address is a macro function defined in glibc-2.27/sysdeps/generic/libc-tsd.h
#define __libc_tsd_address(TYPE, KEY) (&__libc_tsd_##KEY)
So __libc_tsd_address (const uint16_t *, CTYPE_B) will be expanded as &__libc_tsd_CTYPE_B, the address of variable __libc_tsd_CTYPE_B. __libc_tsd_CTYPE_B is a variable pointer to const unsigned short int declared in glibc-2.27/include/ctype.h as follows
__libc_tsd_define (extern, const uint16_t *, CTYPE_B)
__libc_tsd_define is a macro defined in glibc-2.27/sysdeps/generic/libc-tsd.h
#define __libc_tsd_define(CLASS, TYPE, KEY) \
CLASS __thread TYPE __libc_tsd_##KEY attribute_tls_model_ie;
So the declaration of variable __libc_tsd_CTYPE_B is as follows
extern __thread const uint16_t __libc_tsd_CTYPE_B attribute_tls_model_ie;
The value of __libc_tsd_CTYPE_B is initialized when the C program is executed by calling the function _init defined in glibc-2.27/csu/init-first.c. Then the function _init will call function __ctype_init which is used for initializing variable __libc_tsd_CTYPE_B.
Function __ctype_init is declared in glibc-2.27/include/ctype.h
extern void __ctype_init (void);
and defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype-info.c
void
__ctype_init (void)
{
const uint16_t **bp = __libc_tsd_address (const uint16_t *, CTYPE_B);
*bp = (const uint16_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_CLASS) + 128;
const int32_t **up = __libc_tsd_address (const int32_t *, CTYPE_TOUPPER);
*up = ((int32_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER) + 128);
const int32_t **lp = __libc_tsd_address (const int32_t *, CTYPE_TOLOWER);
*lp = ((int32_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER) + 128);
}
Expanding the macro __libc_tsd_address, it becomes as follows
void
__ctype_init (void)
{
const uint16_t **bp = &__libc_tsd_CTYPE_B;
*bp = (const uint16_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_CLASS) + 128;
const int32_t **up = &__libc_tsd_CTYPE_TOUPPER;
*up = ((int32_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER) + 128);
const int32_t **lp = &__libc_tsd_CTYPE_TOLOWER;
*lp = ((int32_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER) + 128);
}
Macro _NL_CURRENT is defined in glibc-2.27/locale/localeinfo.c
#define _NL_CURRENT(category, item) \
((*_nl_current_##category)->values[_NL_ITEM_INDEX (item)].string)
_NL_ITEM_INDEX is a macro defined in glibc-2.27/locale/localeinfo.c
#define _NL_ITEM_INDEX(item) ((int) (item) & 0xffff)
Expanding the macro _NL_CURRENT and _NL_ITEM_INDEX, the function __ctype_init will look as follows
void
__ctype_init (void)
{
const uint16_t **bp = (&__libc_tsd_CTYPE_B);
*bp = (const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128;
const int32_t **up = (&__libc_tsd_CTYPE_TOUPPER);
*up = ((int32_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER) & 0xffff)].string) + 128);
const int32_t **lp = (&__libc_tsd_CTYPE_TOLOWER);
*lp = ((int32_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER) & 0xffff)].string) + 128);
}
Therefore, the function isalpha, isdigit, isalnum, isspace, islower, isupper, isxdigit, iscntrl, isprint, ispunct, isgraph become as follows
int isalnum (int c) { return __isctype (c, _ISalnum); }
int isalpha (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISalpha); }
int iscntrl (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _IScntrl); }
int isdigit (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISdigit); }
int islower (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISlower); }
int isgraph (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISgraph); }
int isprint (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISprint); }
int ispunct (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISpunct); }
int isspace (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISspace); }
int isupper (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISupper); }
int isxdigit (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISxdigit); }
int isblank (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISblank); }
The definition of function tolower and toupper are defined in glibc-2.27/ctype/ctype.c.
#define __ctype_tolower \
((int32_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER) + 128)
#define __ctype_toupper \
((int32_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER) + 128)
int
tolower (int c)
{
return c >= -128 && c < 256 ? __ctype_tolower[c] : c;
}
int
toupper (int c)
{
return c >= -128 && c < 256 ? __ctype_toupper[c] : c;
}
If we expand the macro __ctype_tolower and __ctype_toupper, it becomes as follows
int
tolower (int c)
{
return c >= -128 && c < 256 ? ((int32_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER) + 128)[c] : c;
}
int
toupper (int c)
{
return c >= -128 && c < 256 ? ((int32_t *) _NL_CURRENT (LC_CTYPE, _NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER) + 128)[c] : c;
}
Expanding the macro _NL_CURRENT and _NL_ITEM_INDEX, the function toupper and tolower will look as follows
int
tolower (int c)
{
return c >= -128 && c < 256 ? ((int32_t *) ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[c] : c;
}
int
toupper (int c)
{
return c >= -128 && c < 256 ? ((*_nl_current_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[c] : c;
}
_NL_CTYPE_CLASS, _NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER, and _NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER are enum values defined
in glibc-2.27/locale/langinfo.h
#define _NL_ITEM(category, index) (((category) << 16) | (index))
enum
{
/* LC_TIME category: date and time formatting. */
/* Abbreviated days of the week. */
ABDAY_1 = _NL_ITEM (__LC_TIME, 0), /* Sun */
#define ABDAY_1 ABDAY_1
ABDAY_2,
#define ABDAY_2 ABDAY_2
ABDAY_3,
#define ABDAY_3 ABDAY_3
ABDAY_4,
#define ABDAY_4 ABDAY_4
ABDAY_5,
#define ABDAY_5 ABDAY_5
ABDAY_6,
#define ABDAY_6 ABDAY_6
ABDAY_7,
#define ABDAY_7 ABDAY_7
/* Long-named days of the week. */
DAY_1, /* Sunday */
#define DAY_1 DAY_1
DAY_2, /* Monday */
#define DAY_2 DAY_2
DAY_3, /* Tuesday */
#define DAY_3 DAY_3
DAY_4, /* Wednesday */
#define DAY_4 DAY_4
DAY_5, /* Thursday */
#define DAY_5 DAY_5
DAY_6, /* Friday */
#define DAY_6 DAY_6
DAY_7, /* Saturday */
#define DAY_7 DAY_7
/* Abbreviated month names, in the grammatical form used when the month
is a part of a complete date. */
ABMON_1, /* Jan */
#define ABMON_1 ABMON_1
ABMON_2,
#define ABMON_2 ABMON_2
ABMON_3,
#define ABMON_3 ABMON_3
ABMON_4,
#define ABMON_4 ABMON_4
ABMON_5,
#define ABMON_5 ABMON_5
ABMON_6,
#define ABMON_6 ABMON_6
ABMON_7,
#define ABMON_7 ABMON_7
ABMON_8,
#define ABMON_8 ABMON_8
ABMON_9,
#define ABMON_9 ABMON_9
ABMON_10,
#define ABMON_10 ABMON_10
ABMON_11,
#define ABMON_11 ABMON_11
ABMON_12,
#define ABMON_12 ABMON_12
/* Long month names, in the grammatical form used when the month
is a part of a complete date. */
MON_1, /* January */
#define MON_1 MON_1
MON_2,
#define MON_2 MON_2
MON_3,
#define MON_3 MON_3
MON_4,
#define MON_4 MON_4
MON_5,
#define MON_5 MON_5
MON_6,
#define MON_6 MON_6
MON_7,
#define MON_7 MON_7
MON_8,
#define MON_8 MON_8
MON_9,
#define MON_9 MON_9
MON_10,
#define MON_10 MON_10
MON_11,
#define MON_11 MON_11
MON_12,
#define MON_12 MON_12
AM_STR, /* Ante meridiem string. */
#define AM_STR AM_STR
PM_STR, /* Post meridiem string. */
#define PM_STR PM_STR
D_T_FMT, /* Date and time format for strftime. */
#define D_T_FMT D_T_FMT
D_FMT, /* Date format for strftime. */
#define D_FMT D_FMT
T_FMT, /* Time format for strftime. */
#define T_FMT T_FMT
T_FMT_AMPM, /* 12-hour time format for strftime. */
#define T_FMT_AMPM T_FMT_AMPM
ERA, /* Alternate era. */
#define ERA ERA
__ERA_YEAR, /* Year in alternate era format. */
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define ERA_YEAR __ERA_YEAR
#endif
ERA_D_FMT, /* Date in alternate era format. */
#define ERA_D_FMT ERA_D_FMT
ALT_DIGITS, /* Alternate symbols for digits. */
#define ALT_DIGITS ALT_DIGITS
ERA_D_T_FMT, /* Date and time in alternate era format. */
#define ERA_D_T_FMT ERA_D_T_FMT
ERA_T_FMT, /* Time in alternate era format. */
#define ERA_T_FMT ERA_T_FMT
_NL_TIME_ERA_NUM_ENTRIES, /* Number entries in the era arrays. */
_NL_TIME_ERA_ENTRIES, /* Structure with era entries in usable form.*/
_NL_WABDAY_1, /* Sun */
_NL_WABDAY_2,
_NL_WABDAY_3,
_NL_WABDAY_4,
_NL_WABDAY_5,
_NL_WABDAY_6,
_NL_WABDAY_7,
/* Long-named days of the week. */
_NL_WDAY_1, /* Sunday */
_NL_WDAY_2, /* Monday */
_NL_WDAY_3, /* Tuesday */
_NL_WDAY_4, /* Wednesday */
_NL_WDAY_5, /* Thursday */
_NL_WDAY_6, /* Friday */
_NL_WDAY_7, /* Saturday */
/* Abbreviated month names, in the grammatical form used when the month
is a part of a complete date. */
_NL_WABMON_1, /* Jan */
_NL_WABMON_2,
_NL_WABMON_3,
_NL_WABMON_4,
_NL_WABMON_5,
_NL_WABMON_6,
_NL_WABMON_7,
_NL_WABMON_8,
_NL_WABMON_9,
_NL_WABMON_10,
_NL_WABMON_11,
_NL_WABMON_12,
/* Long month names, in the grammatical form used when the month
is a part of a complete date. */
_NL_WMON_1, /* January */
_NL_WMON_2,
_NL_WMON_3,
_NL_WMON_4,
_NL_WMON_5,
_NL_WMON_6,
_NL_WMON_7,
_NL_WMON_8,
_NL_WMON_9,
_NL_WMON_10,
_NL_WMON_11,
_NL_WMON_12,
_NL_WAM_STR, /* Ante meridiem string. */
_NL_WPM_STR, /* Post meridiem string. */
_NL_WD_T_FMT, /* Date and time format for strftime. */
_NL_WD_FMT, /* Date format for strftime. */
_NL_WT_FMT, /* Time format for strftime. */
_NL_WT_FMT_AMPM, /* 12-hour time format for strftime. */
_NL_WERA_YEAR, /* Year in alternate era format. */
_NL_WERA_D_FMT, /* Date in alternate era format. */
_NL_WALT_DIGITS, /* Alternate symbols for digits. */
_NL_WERA_D_T_FMT, /* Date and time in alternate era format. */
_NL_WERA_T_FMT, /* Time in alternate era format. */
_NL_TIME_WEEK_NDAYS,
_NL_TIME_WEEK_1STDAY,
_NL_TIME_WEEK_1STWEEK,
_NL_TIME_FIRST_WEEKDAY,
_NL_TIME_FIRST_WORKDAY,
_NL_TIME_CAL_DIRECTION,
_NL_TIME_TIMEZONE,
_DATE_FMT, /* strftime format for date. */
#define _DATE_FMT _DATE_FMT
_NL_W_DATE_FMT,
_NL_TIME_CODESET,
/* Long month names, in the grammatical form used when the month
is named by itself. */
__ALTMON_1, /* January */
__ALTMON_2,
__ALTMON_3,
__ALTMON_4,
__ALTMON_5,
__ALTMON_6,
__ALTMON_7,
__ALTMON_8,
__ALTMON_9,
__ALTMON_10,
__ALTMON_11,
__ALTMON_12,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define ALTMON_1 __ALTMON_1
# define ALTMON_2 __ALTMON_2
# define ALTMON_3 __ALTMON_3
# define ALTMON_4 __ALTMON_4
# define ALTMON_5 __ALTMON_5
# define ALTMON_6 __ALTMON_6
# define ALTMON_7 __ALTMON_7
# define ALTMON_8 __ALTMON_8
# define ALTMON_9 __ALTMON_9
# define ALTMON_10 __ALTMON_10
# define ALTMON_11 __ALTMON_11
# define ALTMON_12 __ALTMON_12
#endif
/* Long month names, in the grammatical form used when the month
is named by itself. */
_NL_WALTMON_1, /* January */
_NL_WALTMON_2,
_NL_WALTMON_3,
_NL_WALTMON_4,
_NL_WALTMON_5,
_NL_WALTMON_6,
_NL_WALTMON_7,
_NL_WALTMON_8,
_NL_WALTMON_9,
_NL_WALTMON_10,
_NL_WALTMON_11,
_NL_WALTMON_12,
/* Abbreviated month names, in the grammatical form used when the month
is named by itself. */
_NL_ABALTMON_1, /* Jan */
_NL_ABALTMON_2,
_NL_ABALTMON_3,
_NL_ABALTMON_4,
_NL_ABALTMON_5,
_NL_ABALTMON_6,
_NL_ABALTMON_7,
_NL_ABALTMON_8,
_NL_ABALTMON_9,
_NL_ABALTMON_10,
_NL_ABALTMON_11,
_NL_ABALTMON_12,
/* Abbreviated month names, in the grammatical form used when the month
is named by itself. */
_NL_WABALTMON_1, /* Jan */
_NL_WABALTMON_2,
_NL_WABALTMON_3,
_NL_WABALTMON_4,
_NL_WABALTMON_5,
_NL_WABALTMON_6,
_NL_WABALTMON_7,
_NL_WABALTMON_8,
_NL_WABALTMON_9,
_NL_WABALTMON_10,
_NL_WABALTMON_11,
_NL_WABALTMON_12,
_NL_NUM_LC_TIME, /* Number of indices in LC_TIME category. */
/* LC_COLLATE category: text sorting.
This information is accessed by the strcoll and strxfrm functions.
These `nl_langinfo' names are used only internally. */
_NL_COLLATE_NRULES = _NL_ITEM (__LC_COLLATE, 0),
_NL_COLLATE_RULESETS,
_NL_COLLATE_TABLEMB,
_NL_COLLATE_WEIGHTMB,
_NL_COLLATE_EXTRAMB,
_NL_COLLATE_INDIRECTMB,
_NL_COLLATE_GAP1,
_NL_COLLATE_GAP2,
_NL_COLLATE_GAP3,
_NL_COLLATE_TABLEWC,
_NL_COLLATE_WEIGHTWC,
_NL_COLLATE_EXTRAWC,
_NL_COLLATE_INDIRECTWC,
_NL_COLLATE_SYMB_HASH_SIZEMB,
_NL_COLLATE_SYMB_TABLEMB,
_NL_COLLATE_SYMB_EXTRAMB,
_NL_COLLATE_COLLSEQMB,
_NL_COLLATE_COLLSEQWC,
_NL_COLLATE_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_COLLATE,
/* LC_CTYPE category: character classification.
This information is accessed by the functions in <ctype.h>.
These `nl_langinfo' names are used only internally. */
_NL_CTYPE_CLASS = _NL_ITEM (__LC_CTYPE, 0),
_NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER,
_NL_CTYPE_GAP1,
_NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER,
_NL_CTYPE_GAP2,
_NL_CTYPE_CLASS32,
_NL_CTYPE_GAP3,
_NL_CTYPE_GAP4,
_NL_CTYPE_GAP5,
_NL_CTYPE_GAP6,
_NL_CTYPE_CLASS_NAMES,
_NL_CTYPE_MAP_NAMES,
_NL_CTYPE_WIDTH,
_NL_CTYPE_MB_CUR_MAX,
_NL_CTYPE_CODESET_NAME,
CODESET = _NL_CTYPE_CODESET_NAME,
#define CODESET CODESET
_NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER32,
_NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER32,
_NL_CTYPE_CLASS_OFFSET,
_NL_CTYPE_MAP_OFFSET,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS_MB_LEN,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS0_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS1_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS2_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS3_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS4_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS5_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS6_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS7_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS8_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS9_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS_WC_LEN,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS0_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS1_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS2_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS3_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS4_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS5_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS6_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS7_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS8_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS9_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT0_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT1_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT2_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT3_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT4_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT5_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT6_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT7_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT8_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT9_MB,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT0_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT1_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT2_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT3_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT4_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT5_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT6_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT7_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT8_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT9_WC,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_TAB_SIZE,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_FROM_IDX,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_FROM_TBL,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_TO_IDX,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_TO_TBL,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_DEFAULT_MISSING_LEN,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_DEFAULT_MISSING,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_IGNORE_LEN,
_NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_IGNORE,
_NL_CTYPE_MAP_TO_NONASCII,
_NL_CTYPE_NONASCII_CASE,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_1,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_2,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_3,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_4,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_5,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_6,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_7,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_8,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_9,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_10,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_11,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_12,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_13,
_NL_CTYPE_EXTRA_MAP_14,
_NL_NUM_LC_CTYPE,
/* LC_MONETARY category: formatting of monetary quantities.
These items each correspond to a member of `struct lconv',
defined in <locale.h>. */
__INT_CURR_SYMBOL = _NL_ITEM (__LC_MONETARY, 0),
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define INT_CURR_SYMBOL __INT_CURR_SYMBOL
#endif
__CURRENCY_SYMBOL,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define CURRENCY_SYMBOL __CURRENCY_SYMBOL
#endif
__MON_DECIMAL_POINT,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define MON_DECIMAL_POINT __MON_DECIMAL_POINT
#endif
__MON_THOUSANDS_SEP,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define MON_THOUSANDS_SEP __MON_THOUSANDS_SEP
#endif
__MON_GROUPING,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define MON_GROUPING __MON_GROUPING
#endif
__POSITIVE_SIGN,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define POSITIVE_SIGN __POSITIVE_SIGN
#endif
__NEGATIVE_SIGN,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define NEGATIVE_SIGN __NEGATIVE_SIGN
#endif
__INT_FRAC_DIGITS,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define INT_FRAC_DIGITS __INT_FRAC_DIGITS
#endif
__FRAC_DIGITS,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define FRAC_DIGITS __FRAC_DIGITS
#endif
__P_CS_PRECEDES,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define P_CS_PRECEDES __P_CS_PRECEDES
#endif
__P_SEP_BY_SPACE,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define P_SEP_BY_SPACE __P_SEP_BY_SPACE
#endif
__N_CS_PRECEDES,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define N_CS_PRECEDES __N_CS_PRECEDES
#endif
__N_SEP_BY_SPACE,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define N_SEP_BY_SPACE __N_SEP_BY_SPACE
#endif
__P_SIGN_POSN,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define P_SIGN_POSN __P_SIGN_POSN
#endif
__N_SIGN_POSN,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define N_SIGN_POSN __N_SIGN_POSN
#endif
_NL_MONETARY_CRNCYSTR,
#define CRNCYSTR _NL_MONETARY_CRNCYSTR
__INT_P_CS_PRECEDES,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define INT_P_CS_PRECEDES __INT_P_CS_PRECEDES
#endif
__INT_P_SEP_BY_SPACE,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define INT_P_SEP_BY_SPACE __INT_P_SEP_BY_SPACE
#endif
__INT_N_CS_PRECEDES,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define INT_N_CS_PRECEDES __INT_N_CS_PRECEDES
#endif
__INT_N_SEP_BY_SPACE,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define INT_N_SEP_BY_SPACE __INT_N_SEP_BY_SPACE
#endif
__INT_P_SIGN_POSN,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define INT_P_SIGN_POSN __INT_P_SIGN_POSN
#endif
__INT_N_SIGN_POSN,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define INT_N_SIGN_POSN __INT_N_SIGN_POSN
#endif
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_INT_CURR_SYMBOL,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_CURRENCY_SYMBOL,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_INT_FRAC_DIGITS,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_FRAC_DIGITS,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_P_CS_PRECEDES,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_P_SEP_BY_SPACE,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_N_CS_PRECEDES,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_N_SEP_BY_SPACE,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_INT_P_CS_PRECEDES,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_INT_P_SEP_BY_SPACE,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_INT_N_CS_PRECEDES,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_INT_N_SEP_BY_SPACE,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_P_SIGN_POSN,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_N_SIGN_POSN,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_INT_P_SIGN_POSN,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_INT_N_SIGN_POSN,
_NL_MONETARY_UNO_VALID_FROM,
_NL_MONETARY_UNO_VALID_TO,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_VALID_FROM,
_NL_MONETARY_DUO_VALID_TO,
_NL_MONETARY_CONVERSION_RATE,
_NL_MONETARY_DECIMAL_POINT_WC,
_NL_MONETARY_THOUSANDS_SEP_WC,
_NL_MONETARY_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_MONETARY,
/* LC_NUMERIC category: formatting of numbers.
These also correspond to members of `struct lconv'; see <locale.h>. */
__DECIMAL_POINT = _NL_ITEM (__LC_NUMERIC, 0),
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define DECIMAL_POINT __DECIMAL_POINT
#endif
RADIXCHAR = __DECIMAL_POINT,
#define RADIXCHAR RADIXCHAR
__THOUSANDS_SEP,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define THOUSANDS_SEP __THOUSANDS_SEP
#endif
THOUSEP = __THOUSANDS_SEP,
#define THOUSEP THOUSEP
__GROUPING,
#ifdef __USE_GNU
# define GROUPING __GROUPING
#endif
_NL_NUMERIC_DECIMAL_POINT_WC,
_NL_NUMERIC_THOUSANDS_SEP_WC,
_NL_NUMERIC_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_NUMERIC,
__YESEXPR = _NL_ITEM (__LC_MESSAGES, 0), /* Regex matching ``yes'' input. */
#define YESEXPR __YESEXPR
__NOEXPR, /* Regex matching ``no'' input. */
#define NOEXPR __NOEXPR
__YESSTR, /* Output string for ``yes''. */
#if defined __USE_GNU || (defined __USE_XOPEN && !defined __USE_XOPEN2K)
# define YESSTR __YESSTR
#endif
__NOSTR, /* Output string for ``no''. */
#if defined __USE_GNU || (defined __USE_XOPEN && !defined __USE_XOPEN2K)
# define NOSTR __NOSTR
#endif
_NL_MESSAGES_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_MESSAGES,
_NL_PAPER_HEIGHT = _NL_ITEM (__LC_PAPER, 0),
_NL_PAPER_WIDTH,
_NL_PAPER_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_PAPER,
_NL_NAME_NAME_FMT = _NL_ITEM (__LC_NAME, 0),
_NL_NAME_NAME_GEN,
_NL_NAME_NAME_MR,
_NL_NAME_NAME_MRS,
_NL_NAME_NAME_MISS,
_NL_NAME_NAME_MS,
_NL_NAME_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_NAME,
_NL_ADDRESS_POSTAL_FMT = _NL_ITEM (__LC_ADDRESS, 0),
_NL_ADDRESS_COUNTRY_NAME,
_NL_ADDRESS_COUNTRY_POST,
_NL_ADDRESS_COUNTRY_AB2,
_NL_ADDRESS_COUNTRY_AB3,
_NL_ADDRESS_COUNTRY_CAR,
_NL_ADDRESS_COUNTRY_NUM,
_NL_ADDRESS_COUNTRY_ISBN,
_NL_ADDRESS_LANG_NAME,
_NL_ADDRESS_LANG_AB,
_NL_ADDRESS_LANG_TERM,
_NL_ADDRESS_LANG_LIB,
_NL_ADDRESS_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_ADDRESS,
_NL_TELEPHONE_TEL_INT_FMT = _NL_ITEM (__LC_TELEPHONE, 0),
_NL_TELEPHONE_TEL_DOM_FMT,
_NL_TELEPHONE_INT_SELECT,
_NL_TELEPHONE_INT_PREFIX,
_NL_TELEPHONE_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_TELEPHONE,
_NL_MEASUREMENT_MEASUREMENT = _NL_ITEM (__LC_MEASUREMENT, 0),
_NL_MEASUREMENT_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_MEASUREMENT,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_TITLE = _NL_ITEM (__LC_IDENTIFICATION, 0),
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_SOURCE,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_ADDRESS,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_CONTACT,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_EMAIL,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_TEL,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_FAX,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_LANGUAGE,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_TERRITORY,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_AUDIENCE,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_APPLICATION,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_ABBREVIATION,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_REVISION,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_DATE,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_CATEGORY,
_NL_IDENTIFICATION_CODESET,
_NL_NUM_LC_IDENTIFICATION,
/* This marks the highest value used. */
_NL_NUM
};
_nl_current_LC_CTYPE is a pointer to constant pointer to struct __locale_data declared in glibc-2.27/locale/localeinfo.h
#define DEFINE_CATEGORY(category, category_name, items, a) \
extern __thread struct __locale_data *const *_nl_current_##category \
attribute_hidden attribute_tls_model_ie;
#include "categories.def"
#undef DEFINE_CATEGORY
When it includes file categories.def, it will declare variable _nl_current_LC_CTYPE as follows
extern __thread struct __locale_data *const *_nl_current_LC_CTYPE __attribute__ ((tls_model ("initial-exec")));
struct __locale_data is declared in glibc-2.27/locale/localeinfo.h as follows
struct __locale_data
{
const char *name;
const char *filedata; /* Region mapping the file data. */
off_t filesize; /* Size of the file (and the region). */
enum /* Flavor of storage used for those. */
{
ld_malloced, /* Both are malloc'd. */
ld_mapped, /* name is malloc'd, filedata mmap'd */
ld_archive /* Both point into mmap'd archive regions. */
} alloc;
/* This provides a slot for category-specific code to cache data computed
about this locale. That code can set a cleanup function to deallocate
the data. */
struct
{
void (*cleanup) (struct __locale_data *);
union
{
void *data;
struct lc_time_data *time;
const struct gconv_fcts *ctype;
};
} private;
unsigned int usage_count; /* Counter for users. */
int use_translit; /* Nonzero if the mb*towv*() and wc*tomb()
functions should use transliteration. */
unsigned int nstrings; /* Number of strings below. */
union locale_data_value
{
const uint32_t *wstr;
const char *string;
unsigned int word; /* Note endian issues vs 64-bit pointers. */
}
values __flexarr; /* Items, usually pointers into `filedata'. */
};
Variable _nl_current_LC_CTYPE is initialized in glibc-2.27/locale/lc-type.c.
_NL_CURRENT_DEFINE (LC_CTYPE);
_NL_CURRENT_DEFINE is a macro defined in glibc-2.27/locale/localeinfo.h.
#define _NL_CURRENT_DEFINE(category) \
__thread struct __locale_data *const *_nl_current_##category \
attribute_hidden = &_nl_global_locale.__locales[category]; \
asm (".globl " __SYMBOL_PREFIX "_nl_current_" #category "_used\n" \
_NL_CURRENT_DEFINE_ABS (_nl_current_##category##_used, 2));
#define _NL_CURRENT_DEFINE_ABS(sym, val) ".set " #sym ", " #val
LC_CTYPE is a macro defined in glibc-2.27/locale/locale.h.
#define LC_CTYPE __LC_CTYPE
#define LC_NUMERIC __LC_NUMERIC
#define LC_TIME __LC_TIME
#define LC_COLLATE __LC_COLLATE
#define LC_MONETARY __LC_MONETARY
#define LC_MESSAGES __LC_MESSAGES
#define LC_ALL __LC_ALL
#define LC_PAPER __LC_PAPER
#define LC_NAME __LC_NAME
#define LC_ADDRESS __LC_ADDRESS
#define LC_TELEPHONE __LC_TELEPHONE
#define LC_MEASUREMENT __LC_MEASUREMENT
#define LC_IDENTIFICATION __LC_IDENTIFICATION
__LC_CTYPE is a macro defined in glibc-2.27/locale/bits/locale.h.
#define __LC_CTYPE 0
#define __LC_NUMERIC 1
#define __LC_TIME 2
#define __LC_COLLATE 3
#define __LC_MONETARY 4
#define __LC_MESSAGES 5
#define __LC_ALL 6
#define __LC_PAPER 7
#define __LC_NAME 8
#define __LC_ADDRESS 9
#define __LC_TELEPHONE 10
#define __LC_MEASUREMENT 11
#define __LC_IDENTIFICATION 12
After expanding all the macros, we get the initialization of _nl_current_LC_CTYPE as follows
_thread struct __locale_data *const *_nl_current_LC_CTYPE = &_nl_global_locale.__locales[0]; asm (".globl " "_nl_current_" "LC_CTYPE" "_used\n" ".set " "_nl_current_LC_CTYPE_used" ", " "2");;
_nl_global_locale is a variable of struct __locale_struct. struct __locale_struct
is declared in glibc-2.27/locale/bits/types/__locale_t.h as follows
struct __locale_struct
{
/* Note: LC_ALL is not a valid index into this array. */
struct __locale_data *__locales[13]; /* 13 = __LC_LAST. */
/* To increase the speed of this solution we add some special members. */
const unsigned short int *__ctype_b;
const int *__ctype_tolower;
const int *__ctype_toupper;
/* Note: LC_ALL is not a valid index into this array. */
const char *__names[13];
};
The initialization of variable _nl_global_locale in glibc-2.27/locale/global-locale.c is as follows.
struct __locale_struct _nl_global_locale attribute_hidden =
{
.__locales =
{
#define DEFINE_CATEGORY(category, category_name, items, a) \
[category] = &_nl_C_##category,
#include "categories.def"
#undef DEFINE_CATEGORY
},
.__names =
{
[LC_ALL] = _nl_C_name,
#define DEFINE_CATEGORY(category, category_name, items, a) \
[category] = _nl_C_name,
#include "categories.def"
#undef DEFINE_CATEGORY
},
.__ctype_b = (const unsigned short int *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class + 128,
.__ctype_tolower = (const int *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_tolower + 128,
.__ctype_toupper = (const int *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_toupper + 128
};
After expanding the macros, we get this
struct __locale_struct _nl_global_locale =
{
.__locales =
{
[3] = &_nl_C_LC_COLLATE,
[0] = &_nl_C_LC_CTYPE,
[4] = &_nl_C_LC_MONETARY,
[1] = &_nl_C_LC_NUMERIC,
[2] = &_nl_C_LC_TIME,
[5] = &_nl_C_LC_MESSAGES,
[7] = &_nl_C_LC_PAPER,
[8] = &_nl_C_LC_NAME,
[9] = &_nl_C_LC_ADDRESS,
[10] = &_nl_C_LC_TELEPHONE,
[11] = &_nl_C_LC_MEASUREMENT,
[12] = &_nl_C_LC_IDENTIFICATION,
},
.__names =
{
[6] = _nl_C_name,
[3] = _nl_C_name,
[0] = _nl_C_name,
[4] = _nl_C_name,
[1] = _nl_C_name,
[2] = _nl_C_name,
[5] = _nl_C_name,
[7] = _nl_C_name,
[8] = _nl_C_name,
[9] = _nl_C_name,
[10] = _nl_C_name,
[11] = _nl_C_name,
[12] = _nl_C_name,
},
.__ctype_b = (const unsigned short int *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class + 128,
.__ctype_tolower = (const int *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_tolower + 128,
.__ctype_toupper = (const int *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_toupper + 128
};
So we can rewrite the initialization of _nl_global_locale as follows
_thread struct __locale_data *const *_nl_current_LC_CTYPE = &_nl_C_LC_CTYPE; asm (".globl " "_nl_current_" "LC_CTYPE" "_used\n" ".set " "_nl_current_LC_CTYPE_used" ", " "2");;
_nl_C_LC_CTYPE is a variable of const struct __locale_data defined in glibc-2.27/locale/C-ctype.c.
const struct __locale_data _nl_C_LC_CTYPE attribute_hidden =
{
_nl_C_name,
NULL,
0,
0, /* no file mapped */
{ NULL, }, /* no cached data */
UNDELETABLE,
1, /* Enable transliteration by default. */
NR_FIXED + NR_CLASSES + NR_MAPS,
{
/* _NL_CTYPE_CLASS */
{ .string = _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER */
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_toupper },
/* _NL_CTYPE_GAP1 */
{ .string = NULL },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER */
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_tolower },
/* _NL_CTYPE_GAP2 */
{ .string = NULL },
/* _NL_CTYPE_CLASS32 */
{ .string = _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class32 },
/* _NL_CTYPE_GAP3 */
{ .string = NULL },
/* _NL_CTYPE_GAP4 */
{ .string = NULL },
/* _NL_CTYPE_GAP5 */
{ .string = NULL },
/* _NL_CTYPE_GAP6 */
{ .string = NULL },
/* _NL_CTYPE_CLASS_NAMES */
{ .string = "upper\0" "lower\0" "alpha\0" "digit\0" "xdigit\0" "space\0"
"print\0" "graph\0" "blank\0" "cntrl\0" "punct\0" "alnum\0" },
/* _NL_CTYPE_MAP_NAMES */
{ .string = "toupper\0" "tolower\0" },
/* _NL_CTYPE_WIDTH */
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_width.header },
/* _NL_CTYPE_MB_CUR_MAX */
{ .word = 1 },
/* _NL_CTYPE_CODESET_NAME */
{ .string = _nl_C_codeset },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER32 */
{ .string = (const char *) &_nl_C_LC_CTYPE_toupper[128] },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER32 */
{ .string = (const char *) &_nl_C_LC_CTYPE_tolower[128] },
/* _NL_CTYPE_CLASS_OFFSET */
{ .word = NR_FIXED },
/* _NL_CTYPE_MAP_OFFSET */
{ .word = NR_FIXED + NR_CLASSES },
/* _NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS_MB_LEN */
{ .word = 1 },
/* _NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS0_MB .. _NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS9_MB */
{ .string = "0" },
{ .string = "1" },
{ .string = "2" },
{ .string = "3" },
{ .string = "4" },
{ .string = "5" },
{ .string = "6" },
{ .string = "7" },
{ .string = "8" },
{ .string = "9" },
/* _NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS_WC_LEN */
{ .word = 1 },
/* _NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS0_WC .. _NL_CTYPE_INDIGITS9_WC */
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"0" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"1" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"2" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"3" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"4" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"5" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"6" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"7" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"8" },
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"9" },
/* _NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT0_MB .. _NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT9_MB */
{ .string = "0" },
{ .string = "1" },
{ .string = "2" },
{ .string = "3" },
{ .string = "4" },
{ .string = "5" },
{ .string = "6" },
{ .string = "7" },
{ .string = "8" },
{ .string = "9" },
/* _NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT0_WC .. _NL_CTYPE_OUTDIGIT9_WC */
{ .word = L'0' },
{ .word = L'1' },
{ .word = L'2' },
{ .word = L'3' },
{ .word = L'4' },
{ .word = L'5' },
{ .word = L'6' },
{ .word = L'7' },
{ .word = L'8' },
{ .word = L'9' },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_TAB_SIZE */
{ .word = NTRANSLIT },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_FROM_IDX */
{ .wstr = translit_from_idx },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_FROM_TBL */
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) translit_from_tbl },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_TO_IDX */
{ .wstr = translit_to_idx },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_TO_TBL */
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) translit_to_tbl },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_DEFAULT_MISSING_LEN */
{ .word = 1 },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_DEFAULT_MISSING */
{ .wstr = (uint32_t *) L"?" },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_IGNORE_LEN */
{ .word = 0 },
/* _NL_CTYPE_TRANSLIT_IGNORE */
{ .wstr = NULL },
/* _NL_CTYPE_MAP_TO_NONASCII */
{ .word = 0 },
/* _NL_CTYPE_NONASCII_CASE */
{ .word = 0 },
/* NR_CLASSES wctype_tables */
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_upper.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_lower.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_alpha.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_digit.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_xdigit.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_space.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_print.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_graph.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_blank.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_cntrl.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_punct.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class_alnum.header },
/* NR_MAPS wctrans_tables */
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_map_toupper.header },
{ .string = (const char *) _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_map_tolower.header }
}
};
Finally, we can write the function isalpha, isdigit, isalnum, isspace, islower, isupper, isxdigit, iscntrl, isprint, ispunct, isgraph, tolower and toupper as follows
int isalnum (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISalnum); }
int isalpha (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISalpha); }
int iscntrl (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _IScntrl); }
int isdigit (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISdigit); }
int islower (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISlower); }
int isgraph (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISgraph); }
int isprint (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISprint); }
int ispunct (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISpunct); }
int isspace (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISspace); }
int isupper (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISupper); }
int isxdigit (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISxdigit); }
int isblank (int c) { return ((const uint16_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] & (unsigned short int) _ISblank); }
int tolower (int c) { return c >= -128 && c < 256 ? ((int32_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[c] : c; }
int toupper (int c) { return c >= -128 && c < 256 ? ((int32_t *) ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[c] : c; }
The value of _NL_CTYPE_CLASS is 0 or 0x0 in hexadecimal. The result of 0x0 & 0xffff is 0x0 or 0 in decimal. Therefore, the value of (&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[0].string is the address value of array _NL_CTYPE_CLASS.
_NL_CTYPE_CLASS is an array of constant char defined in glibc-2.27/locale/C-ctype.c.
const char _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class[768] attribute_hidden =
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000"
"\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\003\040"
"\002\040" "\002\040" "\002\040" "\002\040" "\002\000" "\002\000"
"\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000"
"\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000"
"\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\002\000" "\001\140" "\004\300"
"\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300"
"\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300"
"\004\300" "\004\300" "\010\330" "\010\330" "\010\330" "\010\330"
"\010\330" "\010\330" "\010\330" "\010\330" "\010\330" "\010\330"
"\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300"
"\004\300" "\010\325" "\010\325" "\010\325" "\010\325" "\010\325"
"\010\325" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305"
"\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305"
"\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305"
"\010\305" "\010\305" "\010\305" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300"
"\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\010\326" "\010\326" "\010\326"
"\010\326" "\010\326" "\010\326" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306"
"\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306"
"\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306"
"\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\010\306" "\004\300"
"\004\300" "\004\300" "\004\300" "\002\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
"\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000" "\000\000"
;
As an array of constant char, the array contains 768 elements. "\000\000" is a string which consists of 2 characters and \000 is an octal number. When it casts to unsigned short int, the number of elements on the array becomes 384 since the size of every element should be 2 bytes.
Why 384 elements? Because the type of variable that passes the function argument of isalpha, isdigit, isalnum, isspace, islower, isupper, isxdigit, iscntrl, isprint, ispunct, isgraph is either char or unsigned char. The range of char is -128 to 127 where the code values from -128 to -1 are used to represent extended ASCII characters and the code values from 0 to 127 are used to represent ASCII control characters and ASCII printable characters. The range of unsigned char is 0 to 255 where the code values from 0 to 127 are used to represent ASCII control characters and ASCII printable characters and the code values from 128 to 255 are used to represent extended ASCII characters. Therefore, the range of value that passes the function argument is -128 to 255 and its wide is 384.
The code ((&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[((int) (_NL_CTYPE_CLASS) & 0xffff)].string) + 128)[(int) (c)] shows that the zero index of the array is on the 129th element. Since C allows an array have negative index, the index of the 1st element to the 128th element is -128 to -1.
Since the size of each element of the array is 2 bytes, then it consists of 16 bits. Each bit is associated with enum values _ISupper, _ISlower, _ISalpha, _ISdigit, _ISxdigit, _ISspace, _ISprint, _ISgraph, _ISblank, _IScntrl, _ISpunct and _ISalnum.
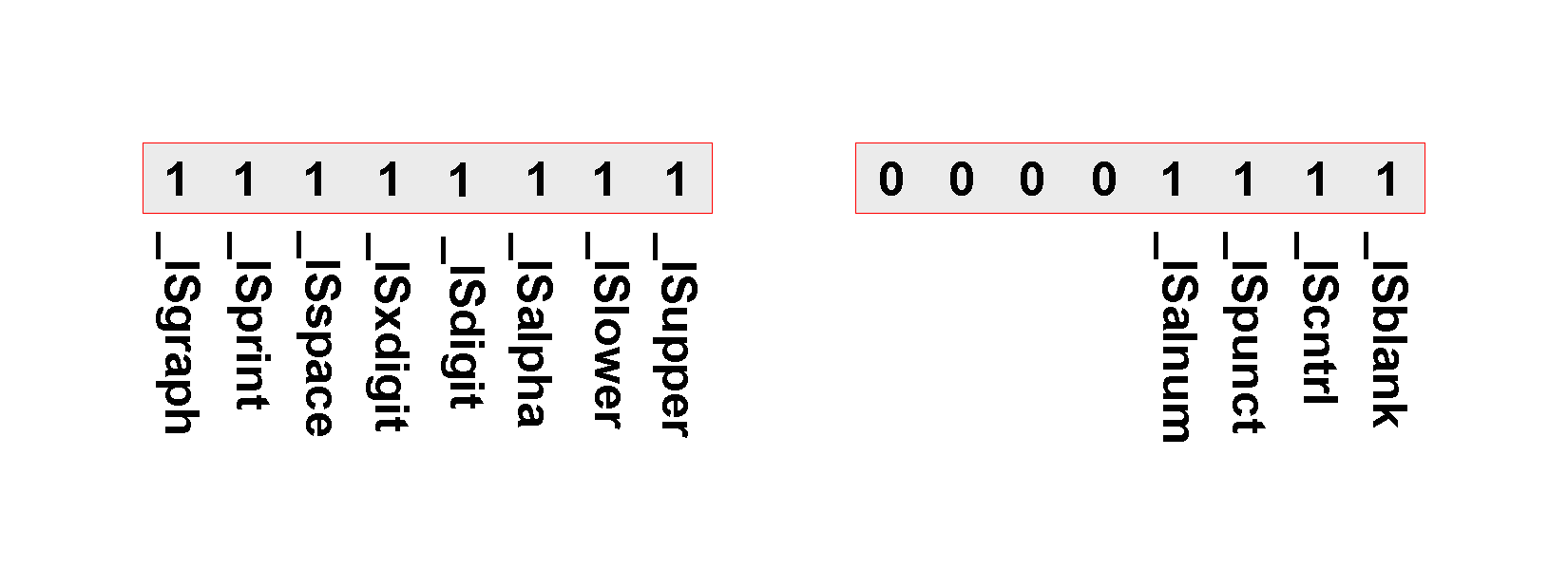
Where does the value "\000\000", "\002\000" or "\003\040" in array
_nl_C_LC_CTYPE_class come from? The 1st element to 128th element are associated with extended ASCII
characters, the 129th element to 255th element are associated with standard ASCII characters and the 256th element to
384th element are also associated with extended ASCII characters.
Since extended ASCII characters are not part of alphanumeric characters or printable characters or graphical characters or any other group, the mask value for it is "\000\000", if it casts to unsigned short int it becomes 00000000 00000000 in binary or 0 in decimal.
Since standard ASCII characters consists alphanumeric characters, printable characters, graphical characters, and other groups then the mask value for it is variant. Characters which are only control characters have mask value "\002\000", if it casts to unsigned short int, it becomes 00000000 00000010 in binary or 2 in decimal and you can see that the 2nd bit is set which is associated with enum value _IScntrl.
Characters which are alphanumeric characters, also graphical characters, also printable characters, also hexadecimal characters, also alphabetic characters and also upper case characters have mask value "\010\325", if it casts to unsigned short int, it becomes 11010101 00001000 in binary or 54536 in decimal. The value 54536 comes from the total sum of _ISalnum, _ISupper, _ISalpha, _ISxdigit, _ISprint and _ISgraph value.
The value of _NL_CTYPE_TOLOWER is 3 or 0x3 in hexadecimal. The result of 0x3 & 0xffff is 0x3 or 3 in decimal. Therefore, the value of (&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[3].string is the address value of array _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_tolower.
_nl_C_LC_CTYPE_tolower is an array of constant unsigned int defined in glibc-2.27/locale/C-ctype.c.
const uint32_t _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_tolower[384] attribute_hidden =
{
/* 0x80 */ 0x80, 0x81, 0x82, 0x83, 0x84, 0x85, 0x86, 0x87,
/* 0x88 */ 0x88, 0x89, 0x8a, 0x8b, 0x8c, 0x8d, 0x8e, 0x8f,
/* 0x90 */ 0x90, 0x91, 0x92, 0x93, 0x94, 0x95, 0x96, 0x97,
/* 0x98 */ 0x98, 0x99, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0x9c, 0x9d, 0x9e, 0x9f,
/* 0xa0 */ 0xa0, 0xa1, 0xa2, 0xa3, 0xa4, 0xa5, 0xa6, 0xa7,
/* 0xa8 */ 0xa8, 0xa9, 0xaa, 0xab, 0xac, 0xad, 0xae, 0xaf,
/* 0xb0 */ 0xb0, 0xb1, 0xb2, 0xb3, 0xb4, 0xb5, 0xb6, 0xb7,
/* 0xb8 */ 0xb8, 0xb9, 0xba, 0xbb, 0xbc, 0xbd, 0xbe, 0xbf,
/* 0xc0 */ 0xc0, 0xc1, 0xc2, 0xc3, 0xc4, 0xc5, 0xc6, 0xc7,
/* 0xc8 */ 0xc8, 0xc9, 0xca, 0xcb, 0xcc, 0xcd, 0xce, 0xcf,
/* 0xd0 */ 0xd0, 0xd1, 0xd2, 0xd3, 0xd4, 0xd5, 0xd6, 0xd7,
/* 0xd8 */ 0xd8, 0xd9, 0xda, 0xdb, 0xdc, 0xdd, 0xde, 0xdf,
/* 0xe0 */ 0xe0, 0xe1, 0xe2, 0xe3, 0xe4, 0xe5, 0xe6, 0xe7,
/* 0xe8 */ 0xe8, 0xe9, 0xea, 0xeb, 0xec, 0xed, 0xee, 0xef,
/* 0xf0 */ 0xf0, 0xf1, 0xf2, 0xf3, 0xf4, 0xf5, 0xf6, 0xf7,
/* 0xf8 */ 0xf8, 0xf9, 0xfa, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0xfd, 0xfe, 0xffffffff,
/* 0x00 */ 0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07,
/* 0x08 */ 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x0f,
/* 0x10 */ 0x10, 0x11, 0x12, 0x13, 0x14, 0x15, 0x16, 0x17,
/* 0x18 */ 0x18, 0x19, 0x1a, 0x1b, 0x1c, 0x1d, 0x1e, 0x1f,
/* 0x20 */ 0x20, 0x21, 0x22, 0x23, 0x24, 0x25, 0x26, 0x27,
/* 0x28 */ 0x28, 0x29, 0x2a, 0x2b, 0x2c, 0x2d, 0x2e, 0x2f,
/* 0x30 */ 0x30, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37,
/* 0x38 */ 0x38, 0x39, 0x3a, 0x3b, 0x3c, 0x3d, 0x3e, 0x3f,
/* 0x40 */ 0x40, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66, 0x67,
/* 0x48 */ 0x68, 0x69, 0x6a, 0x6b, 0x6c, 0x6d, 0x6e, 0x6f,
/* 0x50 */ 0x70, 0x71, 0x72, 0x73, 0x74, 0x75, 0x76, 0x77,
/* 0x58 */ 0x78, 0x79, 0x7a, 0x5b, 0x5c, 0x5d, 0x5e, 0x5f,
/* 0x60 */ 0x60, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66, 0x67,
/* 0x68 */ 0x68, 0x69, 0x6a, 0x6b, 0x6c, 0x6d, 0x6e, 0x6f,
/* 0x70 */ 0x70, 0x71, 0x72, 0x73, 0x74, 0x75, 0x76, 0x77,
/* 0x78 */ 0x78, 0x79, 0x7a, 0x7b, 0x7c, 0x7d, 0x7e, 0x7f,
/* 0x80 */ 0x80, 0x81, 0x82, 0x83, 0x84, 0x85, 0x86, 0x87,
/* 0x88 */ 0x88, 0x89, 0x8a, 0x8b, 0x8c, 0x8d, 0x8e, 0x8f,
/* 0x90 */ 0x90, 0x91, 0x92, 0x93, 0x94, 0x95, 0x96, 0x97,
/* 0x98 */ 0x98, 0x99, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0x9c, 0x9d, 0x9e, 0x9f,
/* 0xa0 */ 0xa0, 0xa1, 0xa2, 0xa3, 0xa4, 0xa5, 0xa6, 0xa7,
/* 0xa8 */ 0xa8, 0xa9, 0xaa, 0xab, 0xac, 0xad, 0xae, 0xaf,
/* 0xb0 */ 0xb0, 0xb1, 0xb2, 0xb3, 0xb4, 0xb5, 0xb6, 0xb7,
/* 0xb8 */ 0xb8, 0xb9, 0xba, 0xbb, 0xbc, 0xbd, 0xbe, 0xbf,
/* 0xc0 */ 0xc0, 0xc1, 0xc2, 0xc3, 0xc4, 0xc5, 0xc6, 0xc7,
/* 0xc8 */ 0xc8, 0xc9, 0xca, 0xcb, 0xcc, 0xcd, 0xce, 0xcf,
/* 0xd0 */ 0xd0, 0xd1, 0xd2, 0xd3, 0xd4, 0xd5, 0xd6, 0xd7,
/* 0xd8 */ 0xd8, 0xd9, 0xda, 0xdb, 0xdc, 0xdd, 0xde, 0xdf,
/* 0xe0 */ 0xe0, 0xe1, 0xe2, 0xe3, 0xe4, 0xe5, 0xe6, 0xe7,
/* 0xe8 */ 0xe8, 0xe9, 0xea, 0xeb, 0xec, 0xed, 0xee, 0xef,
/* 0xf0 */ 0xf0, 0xf1, 0xf2, 0xf3, 0xf4, 0xf5, 0xf6, 0xf7,
/* 0xf8 */ 0xf8, 0xf9, 0xfa, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0xfd, 0xfe, 0xff
};
Each element of array _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_tolower is associated with the ASCII code value in hexadecimal. You can see that the hexadecimal values for capital letters are changed to hexadecimal values for lowercase letters. The hex value for capital a (A) is 0x41 and it is changed to 0x61, hex value for lowercase a as you can see in the array.
The value of _NL_CTYPE_TOUPPER is 2 or 0x2 in hexadecimal. The result of 0x2 & 0xffff is 0x2 or 2 in decimal. Therefore, the value of (&_nl_C_LC_CTYPE)->values[2].string is the address value of array _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_toupper.
_nl_C_LC_CTYPE_toupper is an array of constant unsigned int defined in glibc-2.27/locale/C-ctype.c.
const uint32_t _nl_C_LC_CTYPE_toupper[384] attribute_hidden =
{
/* 0x80 */ 0x80, 0x81, 0x82, 0x83, 0x84, 0x85, 0x86, 0x87,
/* 0x88 */ 0x88, 0x89, 0x8a, 0x8b, 0x8c, 0x8d, 0x8e, 0x8f,
/* 0x90 */ 0x90, 0x91, 0x92, 0x93, 0x94, 0x95, 0x96, 0x97,
/* 0x98 */ 0x98, 0x99, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0x9c, 0x9d, 0x9e, 0x9f,
/* 0xa0 */ 0xa0, 0xa1, 0xa2, 0xa3, 0xa4, 0xa5, 0xa6, 0xa7,
/* 0xa8 */ 0xa8, 0xa9, 0xaa, 0xab, 0xac, 0xad, 0xae, 0xaf,
/* 0xb0 */ 0xb0, 0xb1, 0xb2, 0xb3, 0xb4, 0xb5, 0xb6, 0xb7,
/* 0xb8 */ 0xb8, 0xb9, 0xba, 0xbb, 0xbc, 0xbd, 0xbe, 0xbf,
/* 0xc0 */ 0xc0, 0xc1, 0xc2, 0xc3, 0xc4, 0xc5, 0xc6, 0xc7,
/* 0xc8 */ 0xc8, 0xc9, 0xca, 0xcb, 0xcc, 0xcd, 0xce, 0xcf,
/* 0xd0 */ 0xd0, 0xd1, 0xd2, 0xd3, 0xd4, 0xd5, 0xd6, 0xd7,
/* 0xd8 */ 0xd8, 0xd9, 0xda, 0xdb, 0xdc, 0xdd, 0xde, 0xdf,
/* 0xe0 */ 0xe0, 0xe1, 0xe2, 0xe3, 0xe4, 0xe5, 0xe6, 0xe7,
/* 0xe8 */ 0xe8, 0xe9, 0xea, 0xeb, 0xec, 0xed, 0xee, 0xef,
/* 0xf0 */ 0xf0, 0xf1, 0xf2, 0xf3, 0xf4, 0xf5, 0xf6, 0xf7,
/* 0xf8 */ 0xf8, 0xf9, 0xfa, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0xfd, 0xfe, 0xffffffff,
/* 0x00 */ 0x00, 0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0x06, 0x07,
/* 0x08 */ 0x08, 0x09, 0x0a, 0x0b, 0x0c, 0x0d, 0x0e, 0x0f,
/* 0x10 */ 0x10, 0x11, 0x12, 0x13, 0x14, 0x15, 0x16, 0x17,
/* 0x18 */ 0x18, 0x19, 0x1a, 0x1b, 0x1c, 0x1d, 0x1e, 0x1f,
/* 0x20 */ 0x20, 0x21, 0x22, 0x23, 0x24, 0x25, 0x26, 0x27,
/* 0x28 */ 0x28, 0x29, 0x2a, 0x2b, 0x2c, 0x2d, 0x2e, 0x2f,
/* 0x30 */ 0x30, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33, 0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37,
/* 0x38 */ 0x38, 0x39, 0x3a, 0x3b, 0x3c, 0x3d, 0x3e, 0x3f,
/* 0x40 */ 0x40, 0x41, 0x42, 0x43, 0x44, 0x45, 0x46, 0x47,
/* 0x48 */ 0x48, 0x49, 0x4a, 0x4b, 0x4c, 0x4d, 0x4e, 0x4f,
/* 0x50 */ 0x50, 0x51, 0x52, 0x53, 0x54, 0x55, 0x56, 0x57,
/* 0x58 */ 0x58, 0x59, 0x5a, 0x5b, 0x5c, 0x5d, 0x5e, 0x5f,
/* 0x60 */ 0x60, 0x41, 0x42, 0x43, 0x44, 0x45, 0x46, 0x47,
/* 0x68 */ 0x48, 0x49, 0x4a, 0x4b, 0x4c, 0x4d, 0x4e, 0x4f,
/* 0x70 */ 0x50, 0x51, 0x52, 0x53, 0x54, 0x55, 0x56, 0x57,
/* 0x78 */ 0x58, 0x59, 0x5a, 0x7b, 0x7c, 0x7d, 0x7e, 0x7f,
/* 0x80 */ 0x80, 0x81, 0x82, 0x83, 0x84, 0x85, 0x86, 0x87,
/* 0x88 */ 0x88, 0x89, 0x8a, 0x8b, 0x8c, 0x8d, 0x8e, 0x8f,
/* 0x90 */ 0x90, 0x91, 0x92, 0x93, 0x94, 0x95, 0x96, 0x97,
/* 0x98 */ 0x98, 0x99, 0x9a, 0x9b, 0x9c, 0x9d, 0x9e, 0x9f,
/* 0xa0 */ 0xa0, 0xa1, 0xa2, 0xa3, 0xa4, 0xa5, 0xa6, 0xa7,
/* 0xa8 */ 0xa8, 0xa9, 0xaa, 0xab, 0xac, 0xad, 0xae, 0xaf,
/* 0xb0 */ 0xb0, 0xb1, 0xb2, 0xb3, 0xb4, 0xb5, 0xb6, 0xb7,
/* 0xb8 */ 0xb8, 0xb9, 0xba, 0xbb, 0xbc, 0xbd, 0xbe, 0xbf,
/* 0xc0 */ 0xc0, 0xc1, 0xc2, 0xc3, 0xc4, 0xc5, 0xc6, 0xc7,
/* 0xc8 */ 0xc8, 0xc9, 0xca, 0xcb, 0xcc, 0xcd, 0xce, 0xcf,
/* 0xd0 */ 0xd0, 0xd1, 0xd2, 0xd3, 0xd4, 0xd5, 0xd6, 0xd7,
/* 0xd8 */ 0xd8, 0xd9, 0xda, 0xdb, 0xdc, 0xdd, 0xde, 0xdf,
/* 0xe0 */ 0xe0, 0xe1, 0xe2, 0xe3, 0xe4, 0xe5, 0xe6, 0xe7,
/* 0xe8 */ 0xe8, 0xe9, 0xea, 0xeb, 0xec, 0xed, 0xee, 0xef,
/* 0xf0 */ 0xf0, 0xf1, 0xf2, 0xf3, 0xf4, 0xf5, 0xf6, 0xf7,
/* 0xf8 */ 0xf8, 0xf9, 0xfa, 0xfb, 0xfc, 0xfd, 0xfe, 0xff
};
You can see that the hexadecimal values for lowercase letters are changed to hexadecimal values for capital letters. The hex value for lowercase a is 0x61 and it is changed to 0x41, the hex value for capital a as you can see in the array.


